Chinese Dictionary
Acupuncture
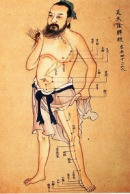
Definition: The Chinese practice of inserting fine needles through the skin at specific points to cure disease or relieve pain.
Details: Acupuncture is in a special category of Han innovations, medicine. This form of treatment is still used in modern China.
Details: Acupuncture is in a special category of Han innovations, medicine. This form of treatment is still used in modern China.
Beijing

Definition: China's capitol.
Details: Host city of the 2008 Olympics, Beijing has many landmarks including Tiananmen Square. Beijing is translated to "northern capitol," while a city south of Beijing is called Nanjing, "southern capitol" (Nanjing is not a capitol of China).
Details: Host city of the 2008 Olympics, Beijing has many landmarks including Tiananmen Square. Beijing is translated to "northern capitol," while a city south of Beijing is called Nanjing, "southern capitol" (Nanjing is not a capitol of China).
Bureacracy
Definition: A body of unelected government officials.
Details: Bureaucracy is based from Confucianism, because Confucius had ideas of ways people and governments should act. One of these ideas was that everyone had a proper role, so if people could earn their way into the government they would be in!
Details: Bureaucracy is based from Confucianism, because Confucius had ideas of ways people and governments should act. One of these ideas was that everyone had a proper role, so if people could earn their way into the government they would be in!
Command Economy
Definition: An economic system in which the central government makes all of the decisions.
Details: China used to be a command economy until the 1970s, when they started allowing certain aspects of a market economy.
Details: China used to be a command economy until the 1970s, when they started allowing certain aspects of a market economy.
Compass

Definition: An instrument that uses Earth's magnetic field to indicate direction.
Details: The compass was invented during the Han Dynasty, but improved during the Tang. This device helped sailors and traders go vast distances on land or water without getting lost. Compasses are still used in present day China and the rest of the world.
Details: The compass was invented during the Han Dynasty, but improved during the Tang. This device helped sailors and traders go vast distances on land or water without getting lost. Compasses are still used in present day China and the rest of the world.
Confucianism

Definition: A philosophy based on the ideas of Confucius that focuses on mortality, family order, social harmony, and government.
Details: A religion that blends elements of Daoism and Buddhism. This religion stresses the importance family, moral values, and respect to elders.
Details: A religion that blends elements of Daoism and Buddhism. This religion stresses the importance family, moral values, and respect to elders.
Daoism

Definition: A philosophy that developed in China and stressed belief that one should live in harmony with the Dao, the guiding force of all reality.
Details: Daoism is based on the teachings of Siddharta Gautama (Buddha). This religion is one of China's most practiced religions.
Details: Daoism is based on the teachings of Siddharta Gautama (Buddha). This religion is one of China's most practiced religions.
Dynasty
Definition: A series of rulers from the same family.
Details: Ancient China's history is divided into dynasties, including the Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han, Sui, Tang, and Song.
Details: Ancient China's history is divided into dynasties, including the Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han, Sui, Tang, and Song.
Forbidden City

Definition: A huge palace complex built by China's Ming emperors that included hundreds of imperial residences, temples, and other government buildings.
Details: This huge city was the pride and joy of the Ming Dynasty because it was inside another city. It is called the forbidden city because normal people, like peasants, were not allowed inside.
Details: This huge city was the pride and joy of the Ming Dynasty because it was inside another city. It is called the forbidden city because normal people, like peasants, were not allowed inside.
Grand Canal
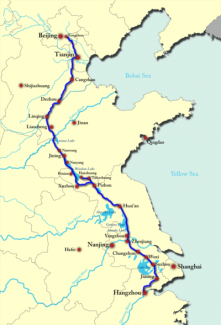
Definition: A canal linking northern and southern China
Details: This canal was started during the Sui Dynasty. The canal was made so northern and southern China could travel and communicate in a fast manner.
Details: This canal was started during the Sui Dynasty. The canal was made so northern and southern China could travel and communicate in a fast manner.
Isolationism
Definition: A policy of avoiding contact with other countries.
Details: When a ruler during the Ming Dynasty called for isolationism in the 1430s, that was a major mistake. This block of to trading and contact to other countries made China's technological advances slow, while the Westerners were making huge advances in the 1800s. And since there was no contact with those countries, China got none of those advances and lost pieces of China.
Details: When a ruler during the Ming Dynasty called for isolationism in the 1430s, that was a major mistake. This block of to trading and contact to other countries made China's technological advances slow, while the Westerners were making huge advances in the 1800s. And since there was no contact with those countries, China got none of those advances and lost pieces of China.
Porcelain

Definition: A thin, beautiful pottery invented in China.
Details: Although it was invented during the Tang Dynasty, it wasn't perfected until hundreds of years later. The Chinese people who worked with this fragile material were considered famous.
Details: Although it was invented during the Tang Dynasty, it wasn't perfected until hundreds of years later. The Chinese people who worked with this fragile material were considered famous.
Great Wall

Definition: A barrier (built to protect China from invasion) that stood near China's northern border.
Details: The wall was started by Shi Huangdi during the Qin Dynasty, it took many years to build. Parts of this huge wall still stand today, drawing in many tourists from China and the rest of the world
Details: The wall was started by Shi Huangdi during the Qin Dynasty, it took many years to build. Parts of this huge wall still stand today, drawing in many tourists from China and the rest of the world
Mandate of Heaven
Definition: The idea that heaven chose China's ruler and gave him or her power.
Details: This idea was inforced during the Zhou Dynasty.
Details: This idea was inforced during the Zhou Dynasty.
Pagodas

Definition: A Buddhist temple based on Indian designs.
Details: Pagodas are multi-storied towers with an upward curving at each floor.
Details: Pagodas are multi-storied towers with an upward curving at each floor.
Scholar Official

Definition: An educated member of China's government who passed a series of written examinations.
Details: After years of studying there would be tests. If you were lucky to have passed high on the tests, you would become a scholar official and perform many important tasks for the government.
Details: After years of studying there would be tests. If you were lucky to have passed high on the tests, you would become a scholar official and perform many important tasks for the government.
Seismograph

Definition: A device the measures the strength of earthquakes.
Details: This was one of the coolest inventions made during the Han Dynasty. The design on the outside of the seismograph relates to another Han advance -- art.
Details: This was one of the coolest inventions made during the Han Dynasty. The design on the outside of the seismograph relates to another Han advance -- art.
Sundial

Definition: A device that uses the position of shadows cast by the sun to tell the time of day.
Details: This device was created during the Han Dynasty. It was the easiest ways to tell time back then.
Details: This device was created during the Han Dynasty. It was the easiest ways to tell time back then.
Tibet

Definition: A Buddhist region in Southwest China.
Details: Tibet has been in China's control since 1950, and Tibetans rebelled in 1959 but was quickly stopped by the Chinese government. The leader, Dalai Lama, had to flee to India.
Details: Tibet has been in China's control since 1950, and Tibetans rebelled in 1959 but was quickly stopped by the Chinese government. The leader, Dalai Lama, had to flee to India.
Woodblock Printing

Definition: A form of printing in which an entire page is carved into a block of wood, covered with ink, and pressed onto a piece of paper to create a printed page.
Details: This is another Tang invention. When woodblock printing, people could copy pictures and texts in a matter of minutes, rather than a bad version in days.
Details: This is another Tang invention. When woodblock printing, people could copy pictures and texts in a matter of minutes, rather than a bad version in days.
In this part of the project, PLP made a dictionary using all of the words listed above. She had to create a description and provide a picture (if able).
